选择排序
关键词:两部分
维基百科
The Selection sort algorithm divides the input list into two parts: the sublist of items already sorted and the sublist of items remaining to be sorted that occupy the rest of the list. Initially, the sorted sublist is empty and the unsorted sublist is the entire input list. The algorithm proceeds by finding the smallest element in the unsorted sublist, exchanging it with the leftmost unsorted element, and moving the sublist boundaries one element to the right.
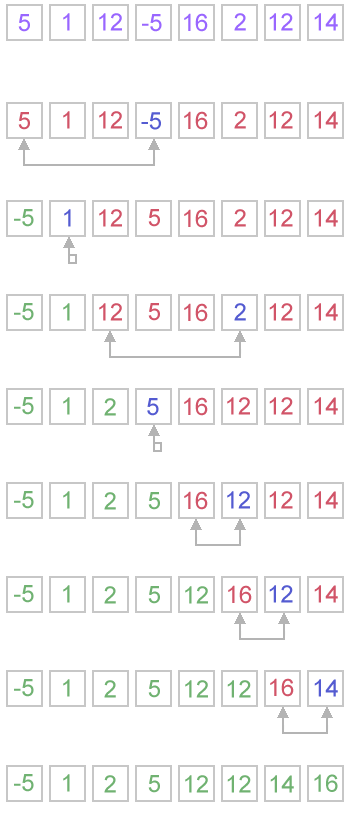
在未排序的那部分中选择最小的元素,然后插入到已排序的那部分中的最右边
复杂度
| 最好 | 平均 | 最差 |
|---|---|---|
| O(n^2) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) |
步骤
C语言实现
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n) {
int i, j, minIndex, tmp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
minIndex = j;
if (minIndex != i) {
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = tmp;
}
}
}
Java语言实现
public void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
int i, j, minIndex, tmp;
int n = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
minIndex = j;
if (minIndex != i) {
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = tmp;
}
}
}